How to Bridge from Boba Network to BNB Chain
Celer cBridge makes it quick, easy, and secure to bridge assets from Boba Network to BNB Chain and from BNB Chain to Boba Network by following these simple steps:
Step 1:
Connect your wallet by clicking on the “Connect Wallet” button above in order to begin your cross-chain transfer.
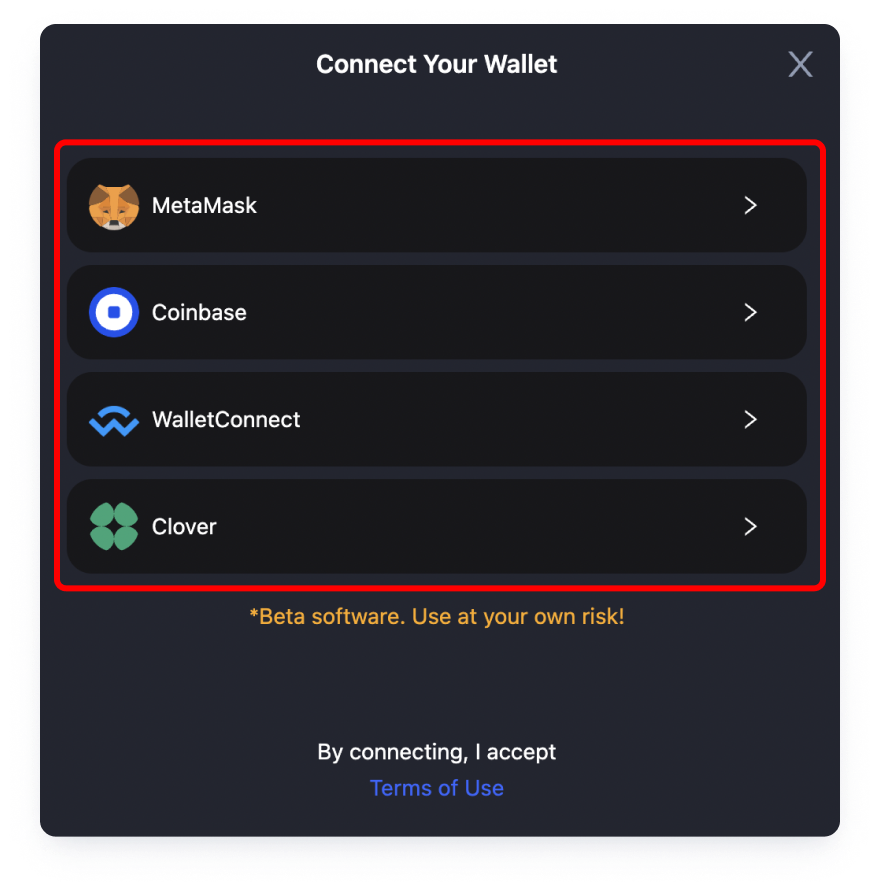
Step 2:
Select “Boba Network” in the “From” dropdown menu, select “BNB Chain” in the “To” dropdown menu, and then select the asset type you wish to bridge to Binance.
Please Note: You will have to switch your wallet’s network to Boba Network in order to perform the cross-chain bridging of your selected token from Boba to Binance.
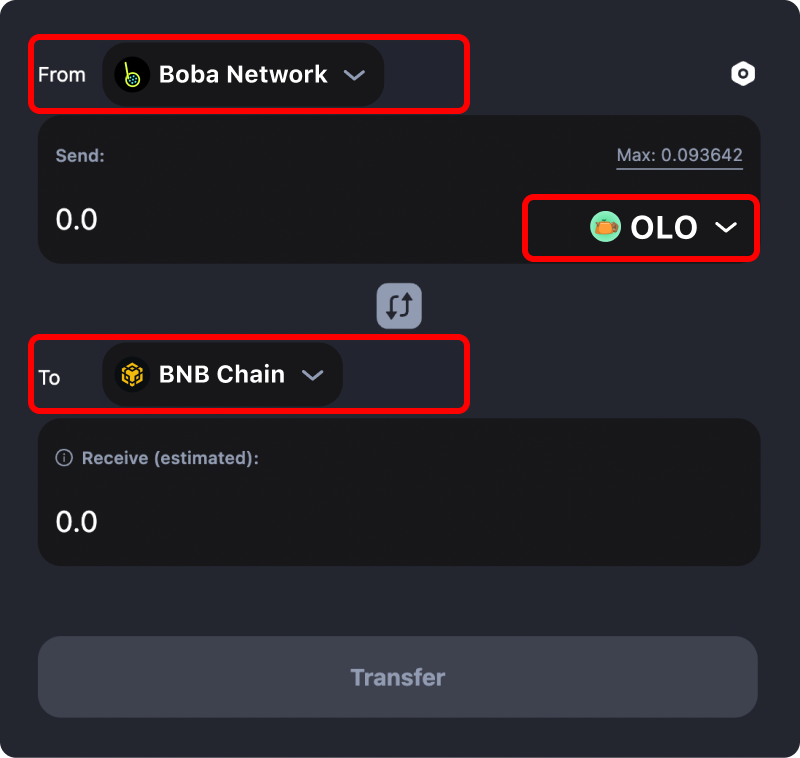
Step 3:
Input the amount of the token you selected that you would like to transfer from Boba to Binance in the “Send:” field. The estimated amount of that asset that is to be bridged to Binance will be displayed in the “Receive (estimated)” field.
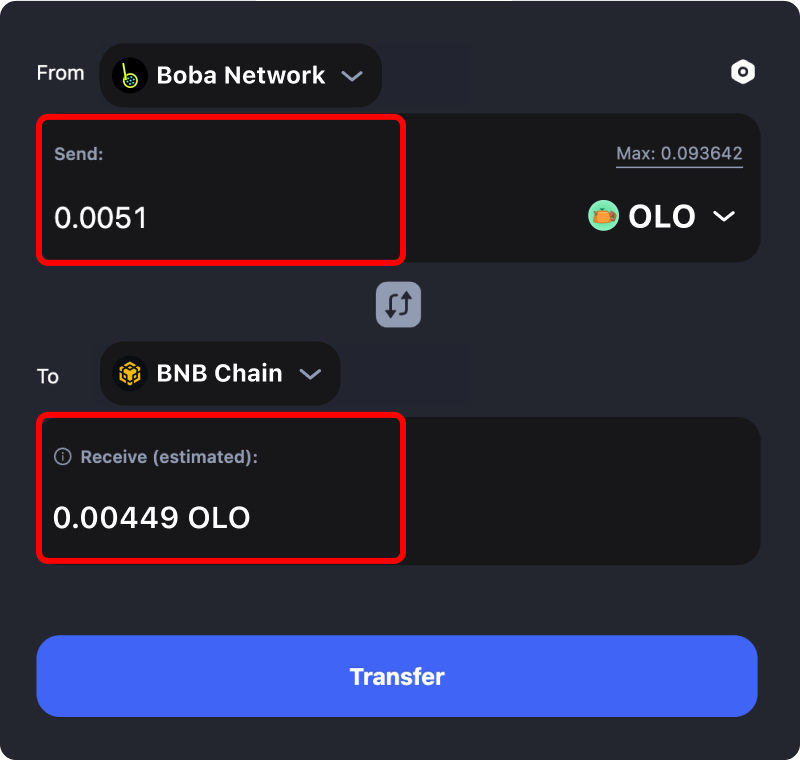
Step 4:
Review all of the Binance bridge transfer information and cost estimates. If all of the cross-chain bridging transaction information is correct and acceptable, click the “Transfer” button and approve the transaction prompts to begin the cross-chain transfer.
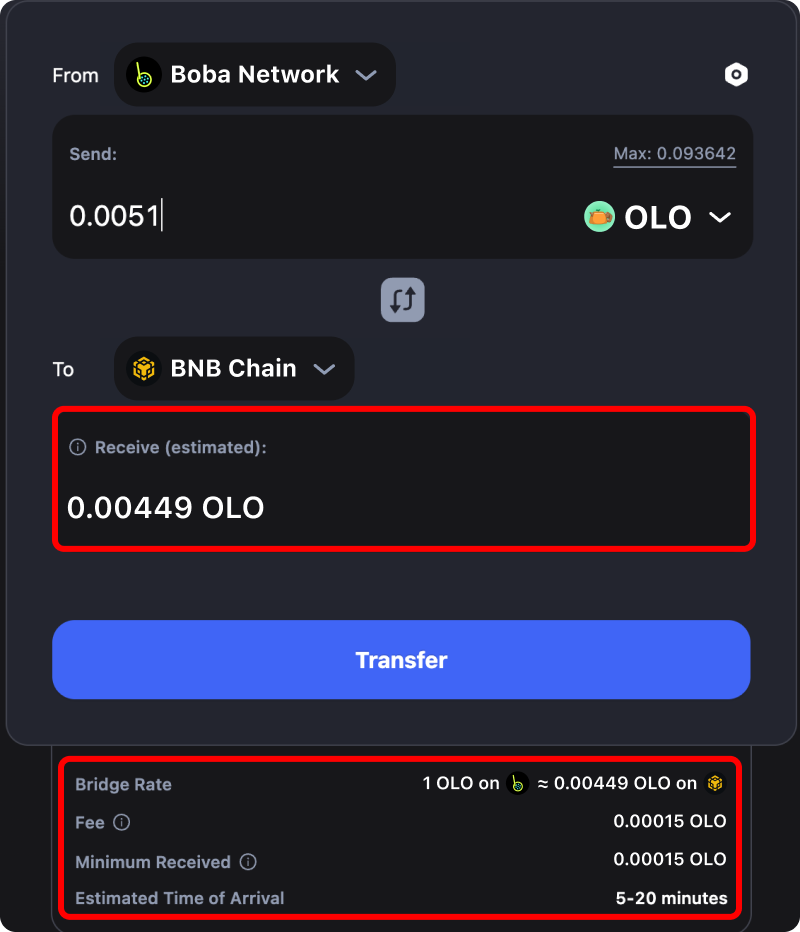
Step 5:
Wait for your cross-chain bridge transaction to BNB Chain to complete. You will then receive your bridged tokens on Binance.
Please Note: Most cross-chain transfers are completed almost instantaneously, however some may take as long as 20 minutes to complete depending on how much traffic the chain is experiencing.
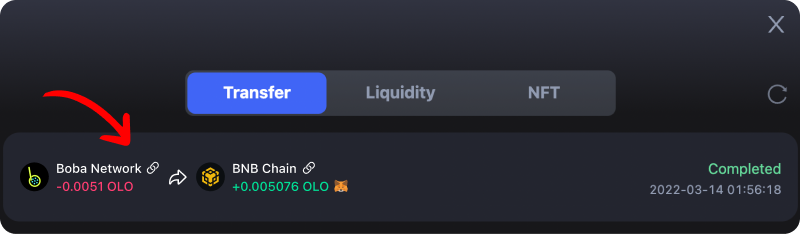
If you wish to see more details about the bridge transaction from Boba to Binance, you can click the links in your “Transfer History” tab.
For a more in-depth step-by-step guide on cross-chain transfers and crypto bridging see our full tutorial here:
https://cbridge-docs.celer.network/tutorial/cross-chain-transfer
Boba Network Information
Formerly known as OMGX, Boba Network is a Layer 2 scaling solution on Ethereum with the focus of reducing transaction costs while increasing transaction speed and throughput to expand the support for the growing ecosystem. Specifically, Boba Network is an Optimistic Rollup, assuming transactions are valid until it is challenged within a time period, where transactions can be verified. Supported by the AI infrastructure company, Enya, and the OMG Foundation, Boba Network was designed as a scalable platform that is EVM compatible and allows developers to quickly develop and deploy their applications. Boba Network is also a hybrid computing platform that not only enables fast transactions with low fees, but also allows smart contracts to execute algorithms directly via the API in order to execute specific functions like machine learning classifications and atomic transactions.
Boba / Ethereum (Boba) Current Information
Description
Similar to other token’s utility for blockchains, the Boba token (BOBA) serves three utilities on the Boba Network: (1). it is the governance token for the Boba DAO where token holders can vote for different initiatives, (2). stakers can receive a portion of the transaction fees earned via on chain distribution in the xBOBA token, a pegged version of BOBA that also has the same DAO voting rights as BOBA, and (3). BOBA can be used to receive a 25% discount on gas fees compared to paying the gas fees with ETH, which is also supported on the Boba Network.
BNB Chain Information
The BNB Chain, often referred to as Binance Smart Chain (BSC) or the Binance Chain, is composed of both the BSC and Binance Chain combined. The BNB Chain (abbreviation for “Build, ‘N Build”) enables BNB Chain governance for things like staking and voting.It also remains Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatible. The BNB Chain aims to increase interoperability across the blockchain ecosystem and develop the core infrastructure to enable and connect the “world’s parallel virtual environment.” With more new and improved features than its two separate parts, the BNB Chain has a boosted BSC throughout, is able to introduce an on-chain governance mechanism, have one-to-many chain scaling, and has overall improved scaling solutions. Plus it has expanded the number of BSC validator sets from 21 to 41!
The six key pillars of the BNB Chain include being permissionless, decentralized, open, multichain accessible, designed for creators and inventors, and with the goal to be bigger than Binance itself.
BNB (BNB) Current Information
Description
BNB is the native cryptocurrency token that fuels the BNB Chain ecosystem and serves as a governance and utility token fueling transactions on the BNB Chain, similar to gas on Ethereum.
Whether you want to simply transfer some BNB between wallets, receive some bridged tokens from another chain like Ethereum Mainnet, or use an application someone has built on BNB; anytime you interact with BNB Chain you will be required to pay a small fee in BNB. BNB can be traded like other cryptocurrencies and widely used in various apps and use cases, including reducing Binance exchange trading fees, paying for transaction fees made via the BNB Chain, and purchasing goods and services online and in-store.
With many large-scale applications in Metaverse, GameFi, SocialFi and others being incorporated into the BNB Chain, Binance is positioning BNB as a token for the Binance ecosystem, which serves several sectors.
Our cross-chain bridge, cBridge, supports the cross-chain bridging of BNB ![]() between multiple chains with the fastest speeds, lowest costs, and most secure transactions available. The full name of this asset is BNB and the ticker of this asset is BNB.
between multiple chains with the fastest speeds, lowest costs, and most secure transactions available. The full name of this asset is BNB and the ticker of this asset is BNB.
What is a Blockchain/Crypto Bridge?
Blockchain or Crypto bridges work just like the real thing, but instead of connecting physical places together, they are used to connect digital ecosystems together. These bridges can pass both information and assets between the bridged blockchains. We call this a cross-chain transfer.
As an example, if you have a need to use a token on BNB Chain, and you have that token on Boba Network and not on BNB Chain, you could either deposit more of that token specifically on BNB Chain, or you could find a Binance bridge that will bridge that from Boba Network to BNB Chain so you do not have to spend more to get additional tokens just because it is on Binance.
There are also different types of bridging in terms of how the cross-chain transfer is done from a technical standpoint. There is liquidity-based bridging where there are liquidity pools of an asset on both the source and destination blockchains. There is also canonical-based bridging where an asset is locked on the source chain and a new asset that represents that locked asset is created on the destination chain.
Bridging and cross-chain transfers are not limited to just normal assets or fungible tokens either. Bridges can transfer and move non-fungible tokens (NFTs) between chains as well. cBridge supports 2 main models when it comes to NFT bridging, pegged NFT bridging and multi-chain native (MCN) NFT bridging. Pegged NFT bridging is similar to the canonical-based bridging mentioned above. The NFT is locked on the source chain and a new NFT that represents that locked NFT is created, or minted, on the destination chain. In the MCN NFT bridging model, however, a MCN NFT does not have the notion of “origin chain” or "original NFT". When transferring an MCN NFT from chain A to chain B, the only pattern is "Burn-and-Mint" so that there is always only one NFT across all of the chains.
Then there are the different levels of “trust” you can have in a crypto bridge. The two main types are trusted and trustless bridges. Trusted bridges depend on a central system or entity and require you to put your trust in them if you wish to use their bridge. Trustless bridges, like our own cBridge, are completely controlled by and run on automated smart contracts and algorithms that have the same security and stability as the blockchain itself.
Things start to get a more complex from there so if you are interested in learning more about the different types of bridges and the tech behind them, you can read through our documents here: https://cbridge-docs.celer.network/
What are the Benefits of Using a Blockchain/Crypto Bridge?
There are many reasons you may want to use a bridge to do a cross-chain transfer between different blockchains:
Lower transaction fees
You can take advantage of platforms with lower transaction fees and higher speeds when compared to more congested chains, like Ethereum Mainnet. Especially when exploring different decentralized applications (dApps). You can look at alternative chains, like BNB Chain, and bridge whatever asset you wish to bridge, from Ethereum to BNB Chain. You can then get some of that chain’s utility token and will be able to enjoy the lower transaction fees and higher speeds afforded to chains like BNB Chain.
Take advantage of other dapps and opportunities on different blockchains
If you’ve been providing liquidity for lending out a certain token on Boba Network, but see that the interest rate for lending that token on BNB Chain is significantly higher; you can use a cross-chain transfer to move your tokens from Boba Network to BNB Chain in order to take advantage of that higher interest rate.
Explore other blockchain ecosystems
The Web3 world is growing fast and you now have more options than ever before when it comes to different blockchains and dApps on those chains. There are many different compelling reasons why developers are building on the chains they are and with all of this diversity it makes it difficult to select a chain to invest in. Bridges and cross-chain transfers help solve this issue. By giving you the ability to bridge assets like ETH, USDT, USDC, and BTC to different chains, this opens up your options when it comes to being able to explore alternate L1 chains and the native dapps and services that they provide.